
PHASE CONTRAST OPTIKAMICROSCOPES
The phase-contrast microscope is a modified version of the bright-field microscope that helps visualize living cells without affecting the cells' viability. It is termed phase-contrast because it consists of a unique phase contrast condenser (annular ring) and a phase contrast objective (phase plate).

Phase Contrast Microscopy Definition, Parts, Uses, Working Principle.
Zernike phase contrast microscopy is extended and combined with a phase-shifting mechanism to perform quantitative phase measurements of microscopic objects. Dozens of discrete point light sources.
Leica DM500 LED Phase Contrast Microscope Slider Phase System New York Microscope Company
In all interferometers, including phase-contrast microscopes 14,15,16,17, DICs 18,19,20,21 (differential interference contrast microscopes) and grating interferometers 22,23, light from a single.

Laboratory Phase Contrast Light Microscope Transmiting Light Microscopes CE A19.2601
Phase-contrast microscopy is an optical microscopy technique that converts phase shifts in the light passing through a transparent specimen to brightness changes in the image. It was first described in 1934 by Dutch physicist Frits Zernike. Principle of Phase contrast Microscopy
IM5 Phase Contrast OPTIKAMICROSCOPES
Phase-contrast microscopy is a method of manipulating light paths through the use of strategically placed rings in order to illuminate transparent objects. Dutch physicist Fritz Zernike developed the technique in the 1930s; for his efforts he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1953. Figure: Phase-contrast microscopy: Phase-contrast image of a cheek.

What Is The Light Source Of Phase Contrast Microscope Design Talk
Phase contrast microscopy is a powerful tool for the characterization of materials at the nanoscale. In this technique, a focused beam of electrons is scanned across a sample to produce a high-resolution image of the surface. It can be used to study various materials, including semiconductors, metals, and insulators.

Figure 5. This diagram of a phasecontrast microscope illustrates phase differences between
This is because an infrared absorption microscope requires a light source in the infrared spectral region, while Raman microscope a visible laser and a spectrometer. Furthermore, both microscope techniques are often operated in a point-scanning detection instead of wide-field imaging with an image sensor.. Molecular-contrast phase-contrast.

Labomed Lx500 Phase Contrast Digital HD Microscope Microscope Central
The Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida, 32310. Phase contrast microscopy, first described in 1934 by Dutch physicist Frits Zernike, is a contrast-enhancing optical technique that can be utilized to produce high-contrast images of transparent specimens such as living cells, microorganisms, thin tissue slices, lithographic patterns.

Motic BA210 Phase Contrast Microscope Microscope Central
The microscope consists of a light source, a phase condenser - to create a narrow, hollow cone of light for illuminating the sample - and a diffraction plate.

Olympus IX50 Inverted Phase Contrast Microscope Microscope Central
Light sources with a uniform phase didn't exist before the invention of the laser (1960s).. Figure 4: Depiction of a phase-contrast microscope light path. The condenser diaphragm is replaced with a phase annulus, that illuminates the sample via the condenser optical elements creating a hollow cone of light. At the objective rear focal.

Motic AE2000 Inverted Phase Contrast Digital Microscope Microscope Central
A light microscope is a biology laboratory instrument or tool, that uses visible light to detect and magnify very small objects and enlarge them. They use lenses to focus light on the specimen, magnifying it thus producing an image. The specimen is normally placed close to the microscopic lens.

Phase Contrast (PCM) Martin Microscope
How to turn your microscope into a phase contrast microscope Gerard 't Hooft Institute for Theoretical Physics Utrecht University Postbox 80.089 3508 TB Utrecht, the Netherlands. lens in such a way that it projects an image of the light source on the disk; consequently, the disk actually blocks the light from entering the microscope, and.
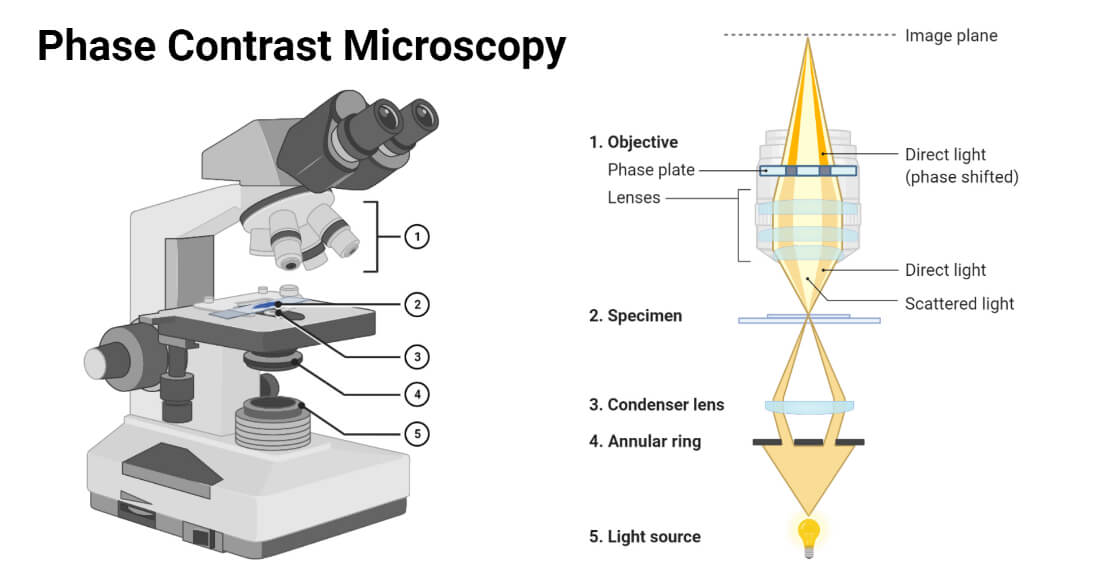
Phase Contrast Microscopy Definition, Principle, Parts, Uses
Phase-contrast microscopy (PCM) is an optical microscopy technique that converts phase shifts in light passing through a transparent specimen to brightness changes in the image. Phase shifts themselves are invisible, but become visible when shown as brightness variations.

Phase contrast microscope Olympus CX43, trinocular, heated stage, HTi 200 Minitube
Phase contrast makes living, unstained microscopic structures visible. Normally the difference in refractive index between a living microscopic structure and its surrounding environment is so small that the structure refracts very little light. Light is, however, diffracted by the specimen.

Phase Contrast AmScope Supplies 40X 1000X 3MP Digital Trinocular LED Infinity Plan Phase
The most important parameter in the basic design of a phase contrast microscope is to isolate the surround and diffracted light waves emerging from the specimen so that they occupy different locations in the diffraction plane at the rear aperture of the objective.

Nikon TMS Inverted Phase Contrast Microscope with HIII Photomicrograp
Phase contrast microscopy, first described in 1934 by Dutch physicist Frits Zernike, is a contrast-enhancing optical technique that can be utilized to produce high-contrast images of transparent specimens, such as living cells (usually in culture), microorganisms, thin tissue slices, lithographic patterns, fibers, latex dispersions, glass fragme.